- Where We Work
- Interactive Map
- Afghanistan and Pakistan
- Africa
- African Union
- Power Africa
- About Us
- How We Work
- Partners
- News & Information
- Power Africa Toolbox
- Where We Work
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Chad
- Côte d`Ivoire
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Djibouti
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Republic of Congo
- Rwanda
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Trade and Investment Engagement
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Central Africa Regional
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Côte d'Ivoire
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Djibouti
- East Africa Regional
- Ethiopia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Republic of the Congo
- Rwanda
- Sahel Regional
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Southern Africa Regional
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Uganda
- West Africa Regional
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
- Asia
- Europe and Eurasia
- Latin America and the Caribbean
- Middle East
- Mission Directory
Republic of Congo
POWER AFRICA FACT SHEET
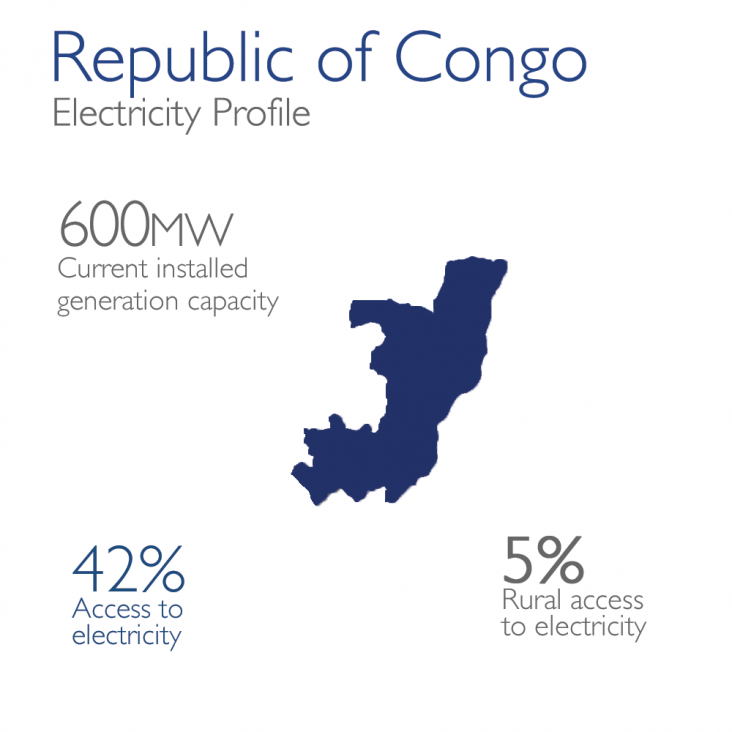
The Republic of Congo’s energy supply is highly dependent on gas (350 MW), hydropower (209 MW), and diesel (41 MW). The country aims to increase its power generation capacity to meet demand, and recently invested in the 120 MW Imboulou hydropower plant, a 30 MW thermal power plant, as well as two 300 MW turbine gas power plants. Due to the deterioration of transmission and distribution facilities, the quality of supplied electricity is poor, and frequently experiences load shedding. The losses in the distribution network stand at above 50%, and the national utility Société Nationale d’Electricité (SNE) must improve its low collection rates, low electricity tariffs and high electricity losses. Based on 2013 data, the Republic of Congo’s national electrification rate reached 42%, (5% in rural areas, 62% in urban areas).
Sources:
- Project Paper on a Proposed Additional Credit and a Proposed Loan to the Republic of Congo for a Water, Electricity and Urban Development Project, World Bank, 2014
- IEA, World Energy Outlook 2015







Comment
Make a general inquiry or suggest an improvement.