
Overview
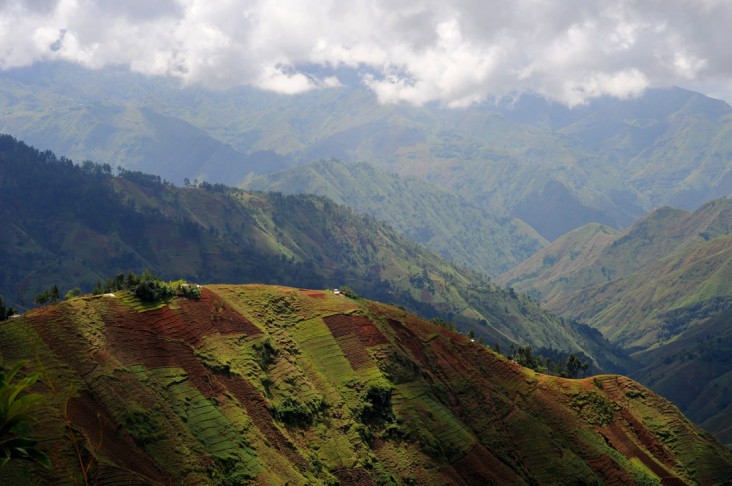
Environmental degradation is a critical concern in Haiti and poses a serious threat to the lives of Haitian citizens. Widespread deforestation, particularly of this mountainous country, has led to flooding, dramatic rates of soil erosion, and subsequent declines in agricultural productivity. Haiti’s valuable coastal and marine resources have been degraded by sediment deposit and overfishing, resulting in considerable loss in biodiversity. In Haiti’s urban areas, waste management is a major challenge, especially in Port-au-Prince, the largest city in the world without a sewer system. Solid waste clogs urban waterways and leads to the spread of waterborne diseases. Landfills are few and do not meet the needs of most municipalities. Medical waste is frequently left untreated, and with incinerators in disrepair is often dumped into open pits to burn or float away during flash floods.
Haiti’s depleted tree cover exacerbates the consequences of storms and hurricanes. Recurring droughts followed by heavy downpours cause frequent flash flooding. In 2016, Haitians finally saw the end of the extreme El Niño drought, the worst in 35 years, which hit the country after two previous years of drought. However, the country was then struck by Hurricane Matthew which devastated parts of Haiti that had been spared the worst of these droughts. The dearth of reliable rainfall in Haiti is not only detrimental to farmers whose crops wilt and die , but also to ordinary Haitians who depend on water catchment systems for their daily water needs.
USAID Strategy and Activities
The strategy of the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) assistance is to help Haiti protect its fragile environment and conserve its precious resources. This approach is incorporated throughout its development portfolio. Focused on sustainable change, USAID helps improve environmentally friendly business and income-generating prospects for Haitians across various sectors and skill levels. To help build a more sustainable Haitian economy, USAID is focused on growing industries that profit from sound management of natural resources and safeguarding the environment while also improving public sector officials’ abilities to respond to this environmental degradation.
Utilizing Technologies in Agriculture: USAID is promoting technologies that increase Haiti’s capacity to adapt to /erratic rainfall, droughts and floods. For example, USAID has introduced the use of greenhouses equipped with drip irrigation and solar panels. This technology allows farmers to focus on high-value horticultural crops while freeing up space for agro-forestry and other reforestation initiatives targeting ecologically vulnerable hillsides.
Promoting market-based solutions to environmental challenges: USAID supports small businesses that decrease the drivers of deforestation by producing charcoal from waste biomass from crops rather than trees and that foster recycling efforts and clear city streets of waste.
Finally, USAID is developing a new reforestation program as well as conservation and environmental rehabilitation activities while also building the capacity of the Government of Haiti and Haitian civil society to foster these same efforts.







Comment
Make a general inquiry or suggest an improvement.